The math behind ray tracing
Table of Contents
In a previous raytracing project, we had to deal basically with two math operations:
- Drawing circles in the screen
- How to propagate traces throughout the screen
Let’s examine in detail how the circle drawing operation was done. The rays will be covered in a future post
Circles#
Consider the following code:
struct Circle {
double x;
double y;
double r;
};
This sctucture covers the most essencial parameters we need to perform math operations with circles.
void FillCircle(SDL_Surface *surface, struct Circle circle, Uint32 color) {
double radius_squared = pow(circle.r, 2);
for (double x = circle.x - circle.r; x <= circle.x + circle.r; x++) {
for (double y = circle.y - circle.r; y <= circle.y + circle.r; y++) {
double distance_squared = pow(x - circle.x, 2) + pow(y - circle.y, 2);
if (distance_squared < radius_squared) {
SDL_Rect pixel = (SDL_Rect){x, y, 1, 1};
SDL_FillRect(surface, &pixel, color);
}
}
}
}
First of all, is important to know that the equation that describes a circle is:
$$ \large (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = r^2 $$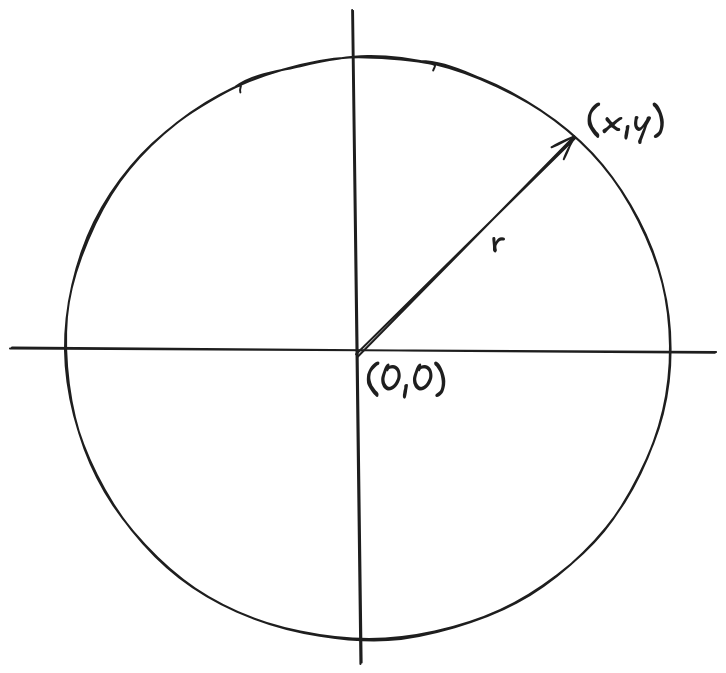
Now, let’s rewrite the cove above in a different way, more like a pseudocode
FillCircle(surface, circle, color) {
// circle.r represents the circle radius
// circle.x represents the center of the circle in the x axis
// circle.y represents the center of the circle in the y axis
// In the circle's equation, the calculus made on the coordinates x and y
// must always be equals to the squared value of the radius of the circle.
// Because of that we store the value of the radius squared (our reference)
// here.
radius_squared = pow(circle.r, 2);
x_leftmost_point = circle.x - circle.r;
x_rightmost_point = circle.x + circle.r;
y_upmost_point = circle.y + circle.r;
y_belowmost_point = circle.y - circle.r;
// If we loop from the leftmost to the rightmost points of the circle
// consequently we will cover all the circle's x axis
for (current_x = x_leftmost_point; current_x <= x_rightmost_point;
current_x++) {
// In a similar way, we're covering all the circle's y axis here.
for (current_y = y_belowmost_point; current_y <= y_upmost_point;
current_y++) {
// In the circle equation, distance_squared represents the left leg
// of the equation
distance_squared = pow(x - circle.x, 2) + pow(y - circle.y, 2);
// Obeying the equation, if the distance_squared is less than
// radius_squared we're inside the circle
if (distance_squared < radius_squared) {
// If we're inside the circle, we colorize the pixel
SDL_Rect pixel = (SDL_Rect){x, y, 1, 1};
SDL_FillRect(surface, &pixel, color);
}
}
}
}
Read other posts